All Products - TPLO Osteotomy Guide v.2
TPLO Osteotomy Guide v.2
Price: Varies
Product Info:
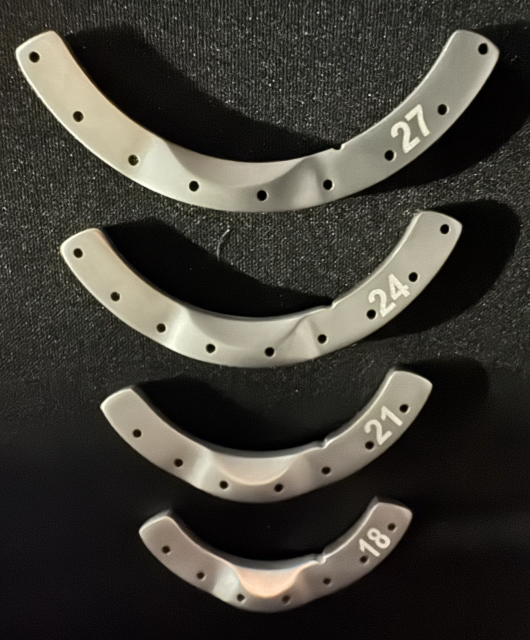
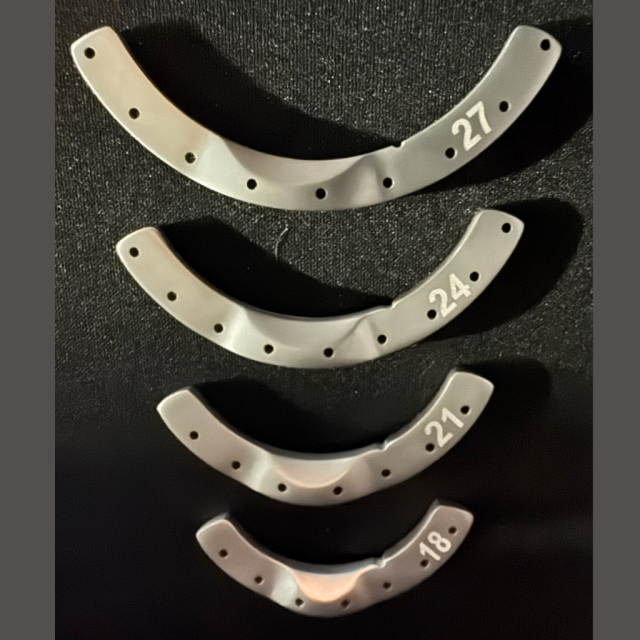
TPLO Osteotomy Guide, V2, 8mm | TOG-V2-8 | $
TPLO Osteotomy Guide, V2, 10 mm | TOG-V2-10 | $
TPLO Osteotomy Guide, V2, 12 mm | TOG-V2-12 | $
TPLO Osteotomy Guide, V2, 15 mm | TOG-V2-15 | $
TPLO Osteotomy Guide, V2, 18 mm | TOG-V2-18 | $275.63
TPLO Osteotomy Guide, V2, 21 mm | TOG-V2-21 | $275.63
TPLO Osteotomy Guide, V2, 24 mm | TOG-V2-24 | $278.91
TPLO Osteotomy Guide, V2, 27 mm | TOG-V2-27 | $278.91
TPLO Osteotomy Guide, V2, 30 mm | TOG-V2-30 | $
TPLO Osteotomy Guide, V2, 33 mm | TOG-V2-33 | $
Email orders to: sales@drmark.vet
One of our staff will contact you to complete your order.
Please include the following in your order email:
- Product name and size
- SKU number
- Quantity for each item
- Shipping address
- Contact name and phone number
TPLO Osteotomy Guide v.2
SKU: TOG-V2-
DESCRIPTION:
TPLO Osteotomy Guide V.2
Refined. Balanced. Built for Precision.
New Design Features:
-
Wider radial body moves pin holes outward, clearing the blade path and stay pins for easier bicortical placement.
-
Sloped "bump" sits flush to the tibia, keeping pin holes perpendicular for stable fixation.
-
Pointed (V-edge) guide reduces blade contact and improves osteotomy precision.
TPLO OSTEOTOMY GUIDE
Precision Guidance for Consistent, Accurate TPLO Osteotomies
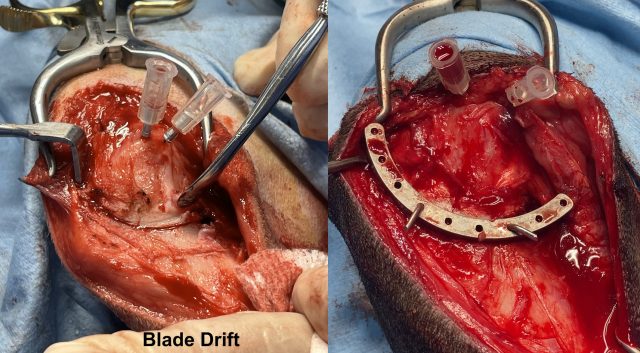
THE CHALLENGE: BLADE DRIFT & INCONSISTENT CUTS
Blade drift is a common cause of inaccurate TPLO osteotomy placement, which can affect rotation, implant fit, and long-term limb function. A low-profile, high-control guide engineered to eliminate drift and improve accuracy, efficiency, and surgical consistency.
THE SOLUTION: A LOW‑PROFILE, HIGH‑CONTROL GUIDE
Eliminates blade drift for precise cut placement.
Low profile allows optimal blade manipulation.
Proximal flare protects the patellar tendon.
Groove landmark provides rotation measurement reference.
Multiple fixation holes for k-wires, stay pins, or point-to-point clamps.
Matches all TPLO crescent blade sizes.
Each guide can be used for left or right stifles.
Durable, reusable medical-grade stainless steel.
AVAILABLE VERSIONS: V.1 AND V.2
Version 1: Features a slim-profile design ideal for routine TPLOs and double-cut techniques.
Version 2: Introduces refined features including a wider radial body, improved clearance for bicortical stay pins, a pointed V-edge for precision, and a sloped bump to keep pin holes perpendicular.
Wider radial body to move pin holes outward
Improved clearance for bicortical stay pins
Pointed V-edge improves osteotomy precision
Sloped bump keeps pin holes perpendicular for stable fixation
Instructions for Use (IFU Summary):
Position guide using D-measurements, implant fit, or surgeon preference.
Secure with at least two 0.045 k-wires angled away from the osteotomy.
Use groove or k-wire technique for rotation measurement.
Align osteotomy blade perpendicular to tibia using guide contour.
Complete osteotomy with controlled blade contact against guide edge.
Rotate proximal segment to alignment landmark.
Stabilize with pin, remove guide, and perform TPLO fixation.
TPLO Osteotomy Guide: Instructions for Use
When performing a TPLO, the osteotomy is one of the most critical aspects of the procedure.
Blade drifting is a common problem when initiating the cut, often resulting in an osteotomy that is not positioned exactly where the surgeon prefers.
The DrMark.Vet Innovations TPLO Osteotomy Guide is designed to address this issue and enhance efficiency and accuracy.
Step 1: Placement
After preparing the proximal tibia and once the surgeon is ready to proceed with the concentric osteotomy, identify the location for placement of the TPLO Osteotomy Guide.
Placement can be determined by: D-measurements, Implant fit, or Surgeon preference.
Pro Tip: Preoperative templating and implant sizing can improve placement accuracy and surgical flow.
Step 2: Positioning and Stabilization
Position the guide with its notch landmark located at the ventro-caudal aspect of the planned osteotomy site, as this will serve as the rotational landmark throughout the procedure.
Stabilize the guide to the tibia by inserting a minimum of two 0.45 k-wires into the predrilled holes of your choice.
Angle the pins away from the osteotomy line to prevent interference with stay pins or the cutting path, and bend the wires to maintain stability.
Pro Tip: Particularly in cases where bone quality is poor, consider using threaded k-wires or VOI Sta-fix pins for improved fixation.
Step 3: Rotational Markers
Once the guide is positioned and securely fastened, measure and mark the distance required for rotation. This can be accomplished using two methods:
The traditional approach involves using an osteotome to create a notch in the proximal segment.
A newer alternative is to place a 0.45 k-wire 2mm off the guide to serve as a rotational marker.
Pro Tip: When using the k-wire method, ensure the wire is not angled into the osteotomy line to avoid contact with the blade during cutting.
Step 4: The Osteotomy
With the guide stabilized, place the osteotomy blade against the guide and orient the blade perpendicular to the tibia.
Perform the cut using the guide's cutting edge to manipulate and fine-tune blade alignment as needed.
Take care to remain within the planned osteotomy line and avoid striking the stabilizing k-wires.
Pro Tip: Do not proceed if the guide feels unstable; repositioning early prevents complications and improves final alignment.
Step 5: Rotation and Final Fixation
Following the osteotomy, rotate the proximal segment until the bone notch or preplaced rotational k-wire aligns with the guide's notch landmark.
Insert a stabilizing pin across the tibial tuberosity and proximal segment to maintain alignment.
Once the osteotomy is stabilized, remove the k-wires and the TPLO Osteotomy Guide, and proceed with TPLO fixation according to your preferred technique.
Conclusion:
Consistent use of these steps, combined with proper preoperative planning and mindful execution, allows the DrMark.Vet TPLO Osteotomy Guide to improve accuracy, reduce intraoperative variability, and produce reliable surgical outcomes.